Drive systems
Polestar combines an internal combustion engine that drives the front wheels with two electric motors that drive the rear wheels.
Two drive systems
Depending on the preselected drive mode and available electric energy, the two drive systems can be used either individually or in parallel.
The electric motors are powered by the hybrid batteries. One of them is located in the tunnel console, while the other is in the luggage compartment, behind the rear seat. The hybrid batteries can be charged in wall sockets, or in a special charging station. The internal combustion engine can also charge the hybrid batteries with a special high-voltage generator.
Both the internal combustion engine and the electric motors can generate motive force directly to the wheels. An advanced control system combines the properties of both drive systems in order to provide optimum driving economy.
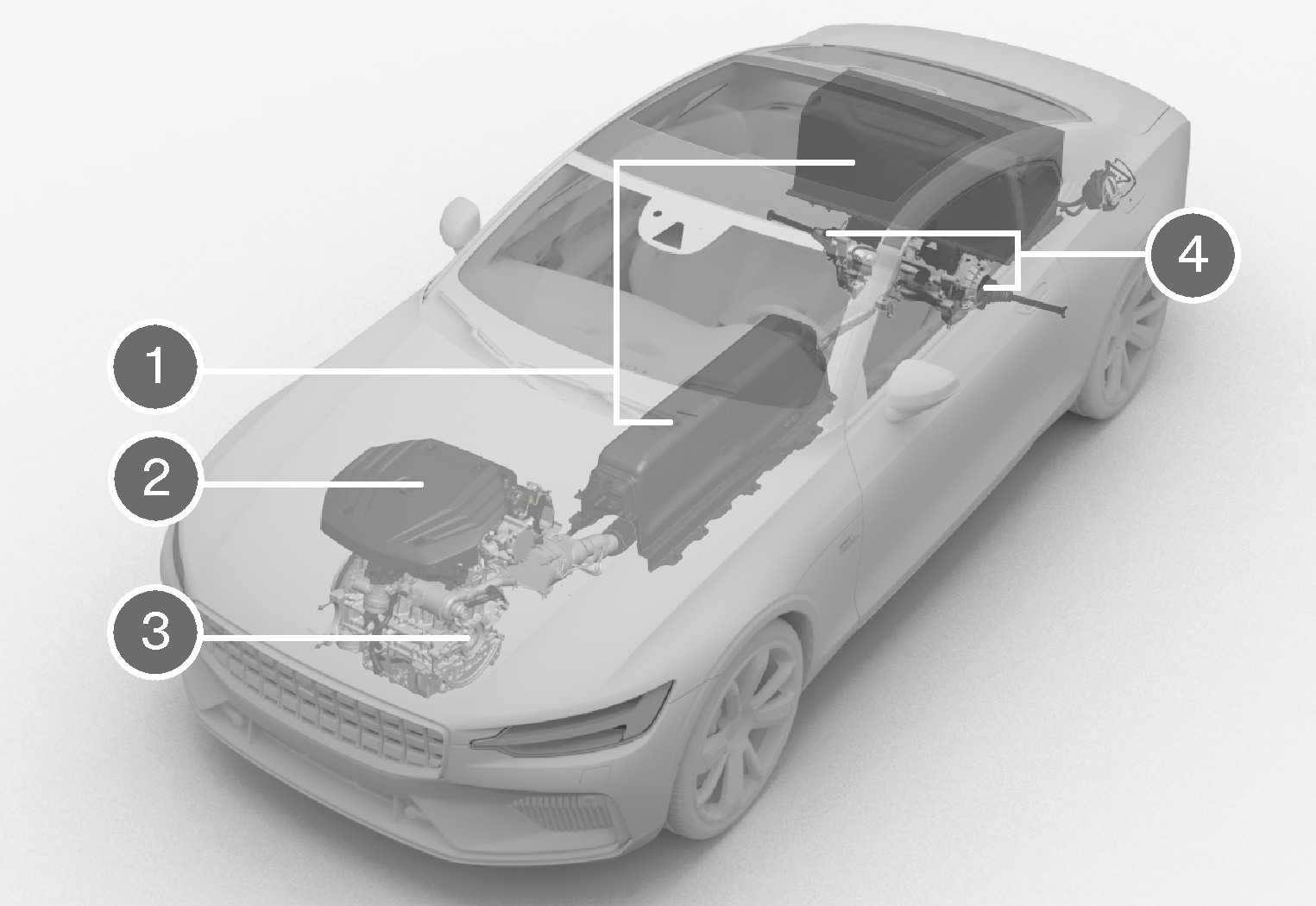
 Hybrid batteries – The car contains two hybrid batteries. The function of these hybrid batteries is to store energy. They receive energy when charging from the mains power circuit, during regenerative braking or from the high-voltage generator. They provide energy for electric operation and preconditioning, for example.
Hybrid batteries – The car contains two hybrid batteries. The function of these hybrid batteries is to store energy. They receive energy when charging from the mains power circuit, during regenerative braking or from the high-voltage generator. They provide energy for electric operation and preconditioning, for example. Internal combustion engine - The internal combustion engine starts when the energy level in the hybrid batteries is insufficient for the engine power that the driver requests.
Internal combustion engine - The internal combustion engine starts when the energy level in the hybrid batteries is insufficient for the engine power that the driver requests. High-voltage generator1 – The high-voltage generator charges the hybrid batteries and also acts as a starter motor for the internal combustion engine. Can support the internal combustion engine with extra electrical energy.
High-voltage generator1 – The high-voltage generator charges the hybrid batteries and also acts as a starter motor for the internal combustion engine. Can support the internal combustion engine with extra electrical energy. Electric motors – The car contains two electric motors that drive the car when it is set to electric operation. They provide additional torque and power on acceleration where necessary, as well as electric four-wheel-drive functionality. The electric motors provide adapted power to each of the rear wheels for additional stability2, e.g. when cornering. They recover brake energy and create electrical energy.
Electric motors – The car contains two electric motors that drive the car when it is set to electric operation. They provide additional torque and power on acceleration where necessary, as well as electric four-wheel-drive functionality. The electric motors provide adapted power to each of the rear wheels for additional stability2, e.g. when cornering. They recover brake energy and create electrical energy.